Skin1004 Madagascar Centella Asiatica 100 Ampoule
100% Centella extract to calm visible redness and heat sensations while supporting a stressed skin barrier.
- Lightweight, layerable
- Helps reduce reactivity
- Use AM/PM after cleansing
Personalised plans to calm redness, reduce flare-ups and improve skin comfort. We assess triggers, skin barrier status and vascular components before recommending care.
Rosacea varies by subtype (erythematotelangiectatic, papulopustular, phymatous, ocular). We tailor care to your presentation.
Common triggers include heat, spicy foods, alcohol, hot drinks, intense exercise, strong wind/sun, stress and fragranced/harsh skincare. A simple diary helps spot patterns.
Over-cleansing and exfoliation worsen reactivity. We prioritise gentle cleansing, consistent UV protection and barrier-repair actives to reduce flare frequency.
Mild, non-foaming cleansers; lukewarm water; pat dry. Avoid scrubs/peels unless clinician-advised.
Ceramides, glycerin, niacinamide (low %) and soothing botanicals can help comfort sensitive skin.
High-protection, broad-spectrum SPF—mineral filters often feel gentler. Reapply during prolonged exposure.
Selected light-based approaches can help with background redness and visible vessels. We’ll advise suitability and realistic expectations at consultation.
Calming facials, barrier-rebuild plans and stepwise actives to reduce triggers and improve comfort. Prescription options available via referral where indicated.
All interventions are subject to consultation — suitability depends on rosacea subtype, vessel pattern, skin sensitivity and overall health. Some treatments are not appropriate for every client.
Targets visible small vessels and persistent redness. Can reduce telangiectasia and flushing with staged sessions.
Non-invasive, soothing light therapy that calms inflammation, supports barrier function and may reduce flare frequency.
A very mild AHA peel that may help with background redness and texture without harshness.
Reserved for specific cases (e.g., phymatous change). Requires careful specialist assessment and follow-up.
Subtype assessment, trigger review and skin exam. We align goals and set a practical plan you can live with.
We start conservatively, review your response and adjust. Education and consistency are the foundation.
Rosacea can relapse. Periodic check-ins help maintain gains and adapt to seasons, lifestyle and stress.
Images shown with permission. Individual results vary; a consultation is required to confirm suitability and set expectations.
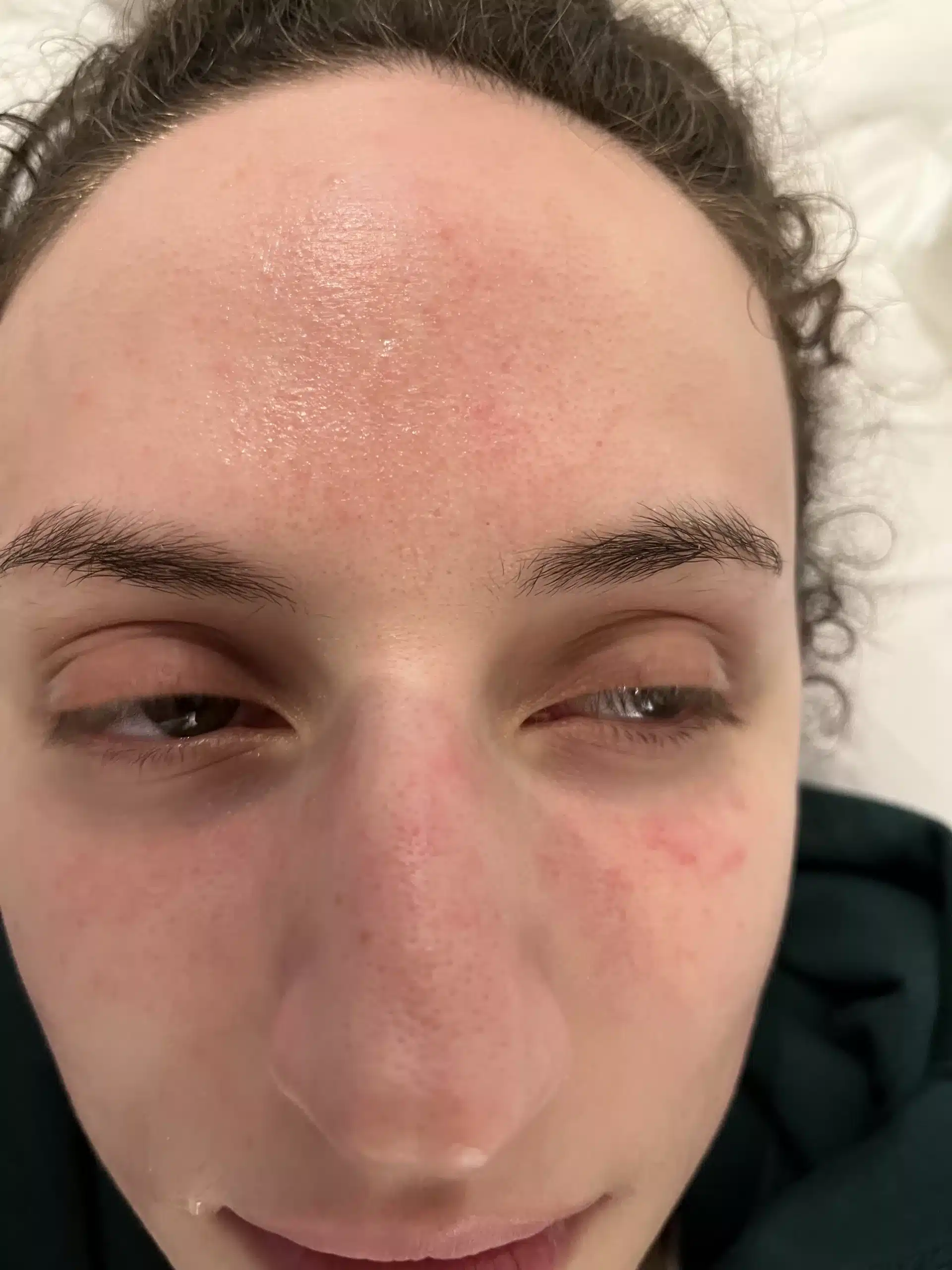
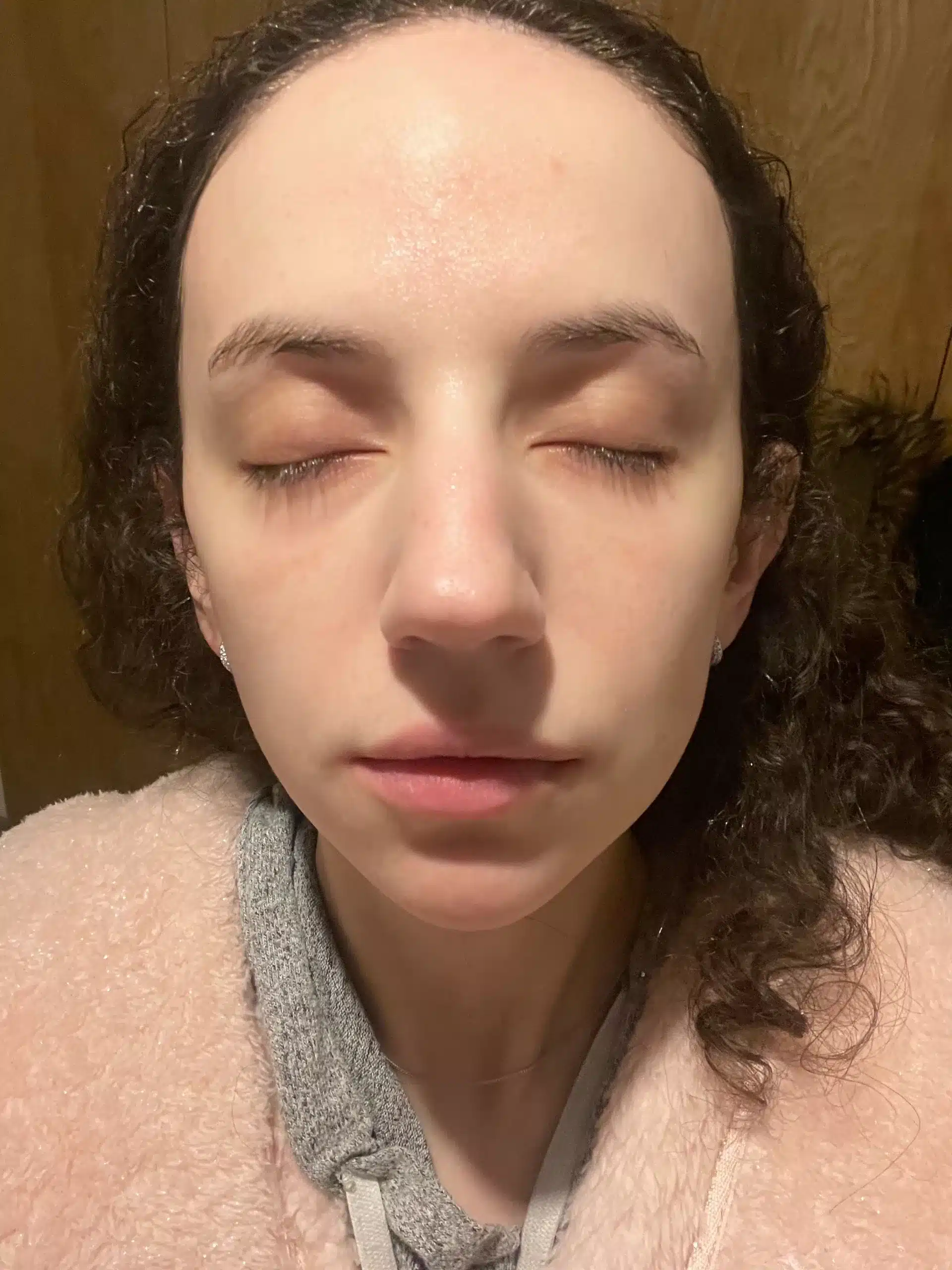
For rosacea-prone skin we keep routines simple: gentle cleanse → soothe & support barrier → daily mineral SPF. Introduce one new product at a time and patch test first.
100% Centella extract to calm visible redness and heat sensations while supporting a stressed skin barrier.
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) mist to gently calm, support the skin’s natural defences, and reduce post-flare discomfort.
Mild, low-pH mousse cleanser that respects barrier lipids while removing impurities without tightness.
Mineral filters (zinc/titanium) often feel kinder to reactive skin. Reapply during prolonged exposure.
Low-dose niacinamide can help support barrier and reduce redness. Start 2–3×/week to assess tolerance.
Important: Always patch test. If irritation occurs, discontinue and consult us. Prescription options may be indicated for certain subtypes.
Rosacea is typically chronic/relapsing. While not “curable”, many people achieve excellent control with trigger management, barrier care and appropriate in-clinic options.
Suitability depends on your skin, subtype and vessel pattern. We’ll discuss benefits and limitations and may suggest a staged approach.
These can help certain subtypes. If indicated, we’ll arrange or liaise for a prescription as part of your plan.
Barrier improvements can be felt within weeks; redness changes often take multiple steps and reviews. We’ll set expectations clearly at your consult.
Medical disclaimer: general information only; not a substitute for medical advice. We’ll assess suitability and discuss alternatives where more appropriate (for example ocular/phymatous types).
WhatsApp us